1. AI Explorer: The "Photographic Memory" Revolution
The defining feature of Windows 12 is internally called "Advanced AI Explorer." Think of it as the spiritual successor to the failed Windows 10 "Timeline," but powered by a local Large Language Model (LLM).
How It Works:
Windows 12 continuously processes information on your screen in the background. It doesn't just look at file names; it looks at context. It indexes conversations in chat apps, specific slides in a PowerPoint presentation, and even frames in a video.
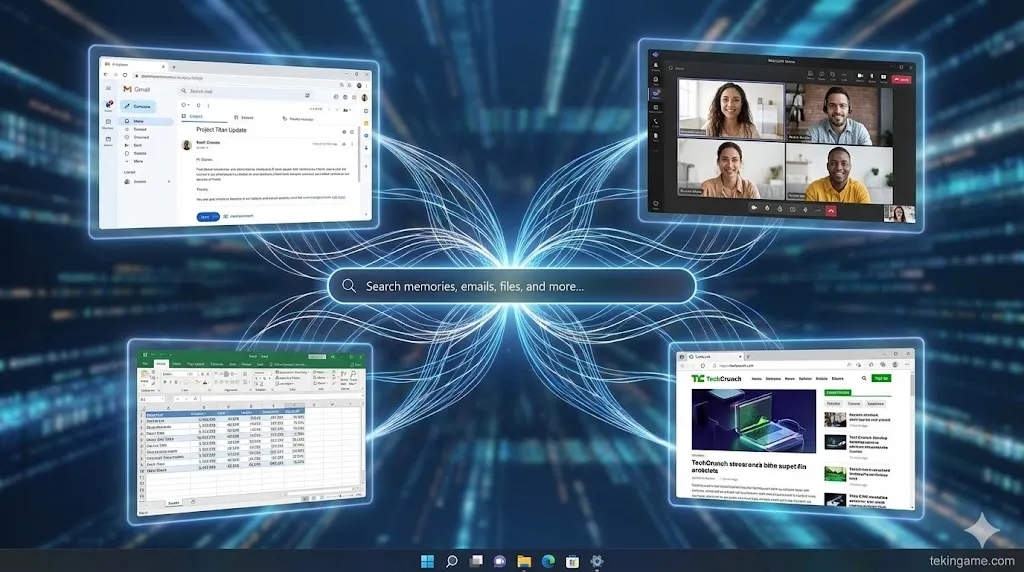
The Use Case: Imagine you are looking for a document. You don't remember the file name, but you remember Jason sent it to you about three weeks ago and it mentioned "Q3 Budget." Instead of searching for filenames, you simply type (or say): "Show me the budget file Jason sent me." The AI Explorer uses natural language processing (NLP) to search its semantic index, understands who "Jason" is, identifies the context of "Budget," and retrieves the exact moment and file instantly. It effectively solves the problem of file management for casual users.
2. CorePC Architecture: Windows Goes Modular
For decades, Windows has been "heavy," burdened by 30 years of legacy code. Project CorePC is Microsoft's attempt to modernize the foundation.
State Separation:
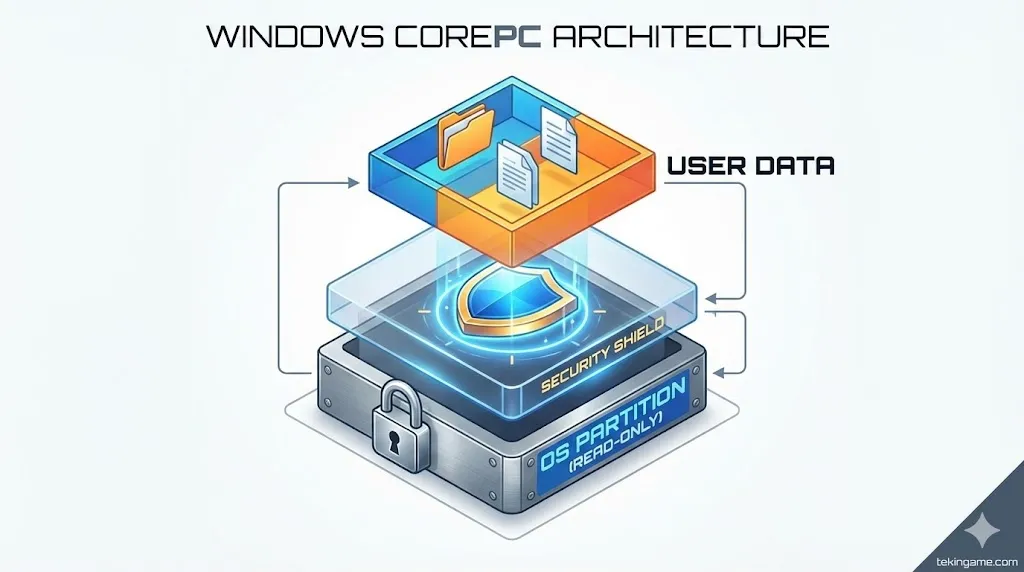
Windows 12 adopts a mobile-like architecture called "State Separation." The operating system files, drivers, and user data are split into completely isolated, read-only partitions.
- Lightning Updates: Because the OS partition is separate, Windows updates can download in the background to a secondary partition. When you restart, the system simply swaps the boot partition. The famous "Do not turn off your PC" screen that lasts 30 minutes? It's gone. Updates now take less than 60 seconds.
- Security: Malware cannot easily infect system files because the system partition is locked (Read-Only) by default.
- Power Reset: "Resetting" your PC to factory settings will be as fast and clean as resetting an iPad.
3. The UI Shift: Floating Taskbar
Visually, Windows 12 is moving towards a design language rumored to be called "Oxygen." The most controversial change is the Floating Taskbar. Instead of being glued to the bottom bezel, the taskbar floats slightly above the bottom of the screen with rounded corners, similar to macOS or iPadOS.
Furthermore, leaks suggest a new Top Bar (System Status Area) that houses the clock, battery, and notification center, freeing up the bottom dock exclusively for applications. This suggests a heavy focus on touch optimization and 2-in-1 devices.
4. Brutal Requirements: The End of 8GB
This is where the backlash begins. Windows 12 is heavy on AI, and AI is heavy on memory.
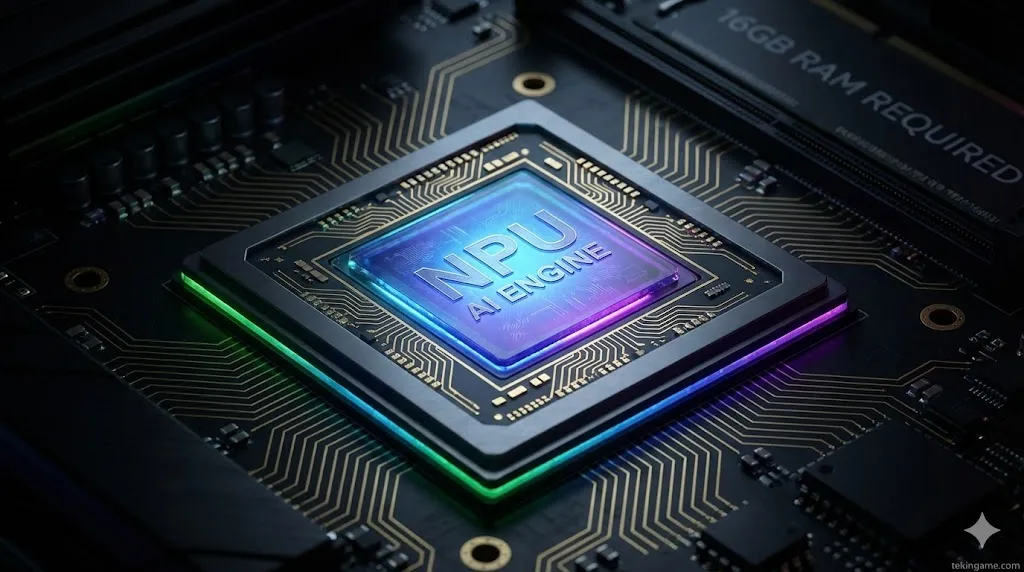
- RAM: The era of 8GB laptops is officially over. The minimum requirement is jumping to 16GB of LPDDR5 RAM. The local AI models need a dedicated memory pool to function without lagging the system.
- The NPU Mandate: To run AI Explorer, you need a Neural Processing Unit (NPU) capable of at least 40 TOPS (Trillion Operations Per Second). This means older Intel Core (13th/14th gen) and Ryzen 5000/6000 CPUs might be compatible with the OS, but they will be locked out of the flagship AI features.
- Storage: Spinning Hard Drives (HDD) are no longer supported as boot drives. SSD is mandatory.

5. Gaming: "Auto Super Resolution"
For gamers, Windows 12 brings a system-level feature called "Auto SR" (Super Resolution). Currently, games need to specifically support DLSS (Nvidia) or FSR (AMD). Windows 12 aims to apply AI upscaling at the OS level.
This means you could play an older game (like Skyrim or Fallout 4), and Windows 12 uses the NPU to upscale it from 1080p to 4K in real-time, sharpening textures and improving frame rates without the game developers needing to issue a patch. It is a game-changer for preserving gaming history.

6. The Privacy Dilemma: The "Big Brother" OS?
The idea of an OS that "records and understands everything on your screen" is a privacy advocate's nightmare. Microsoft is trying to get ahead of the controversy with two promises:
- Local Processing: The AI Explorer index lives on your device. The data is not sent to the cloud to train OpenAI's models.
- Privacy Controls: Users can set "Blacklisted Apps." For example, you can tell Windows to never record the screen when your Banking App or Incognito Browser is open.
However, for enterprise environments, many IT admins are already planning to disable this feature via Group Policy on Day 1.
7. Release Date & Price: Summer 2026
Microsoft follows a specific engineering cycle. The "Platform" version (Germanium) will be ready by June 2026 for OEMs to load onto new laptops.
The General Availability (GA) for the public is scheduled for September or October 2026. As for the price? It will likely be a free upgrade for Windows 11 users, but rumors persist that some "Pro" AI features might be locked behind a Microsoft 365 subscription. The era of the "Subscription OS" might finally be here.
